An approximately 50-meter-high earth dam has been designed in South Kalimantan, about 100 km to the north from Banjarmasin City, named Riam Kiwa. The Indonesian seismic zone map was used as the basis to analyze the seismic load of the project. Upon the design phase completion, the authority required a specific seismic hazard analysis to be performed for the dam. A probabilistic hazard analysis must be determined, in which, its results would be used to perform a time history analysis, followed by dynamic stability analysis.
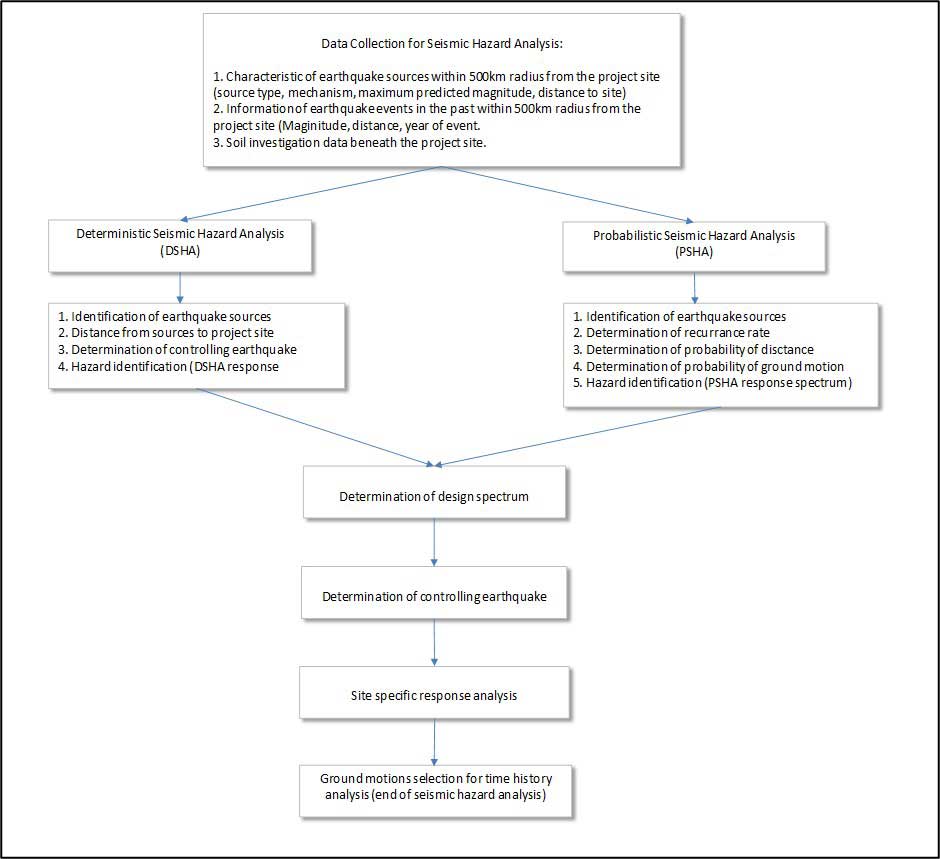
There are (at least) 4 main data required for a seismic hazard analysis, such as:
Earthquake data and time history records are usually gathered from online platforms, while earthquake sources characteristics obtained from literature study. In this project, additional geology data was acquired by installing 4 seismographs in the vicinity of the dam, to determine whether new sources are apparent. A reasonable assumption for shear wave velocity values were taken based on bore log data.
The seismic hazard analysis was completed based on deterministic and probabilistic approaches. Both approaches utilized the latest GMPE (Ground Motion Prediction Equation) commonly used in recent earthquake engineering field. For this project, the probabilistic method governs the design with earthquake return periods of 10.000 years for Safety Evaluation Earthquake (SEE) scenario and 145 years for Operational Based Earthquake (OBE) scenario. 7 (seven) time-history data were collected for each scenario and were adjusted using software to match the design earthquake as close as possible. The Peak Ground Acceleration (PGA) obtained from the hazard analysis was 0.1274 g and 0.067g for SEE and OBE scenario, respectively. The PGA and the ground motions selected were the main input for the time history dynamic analysis of the dam.
General execution flow chart :